Design & Creative Thinking Development Toolkit
Back to Toolkit start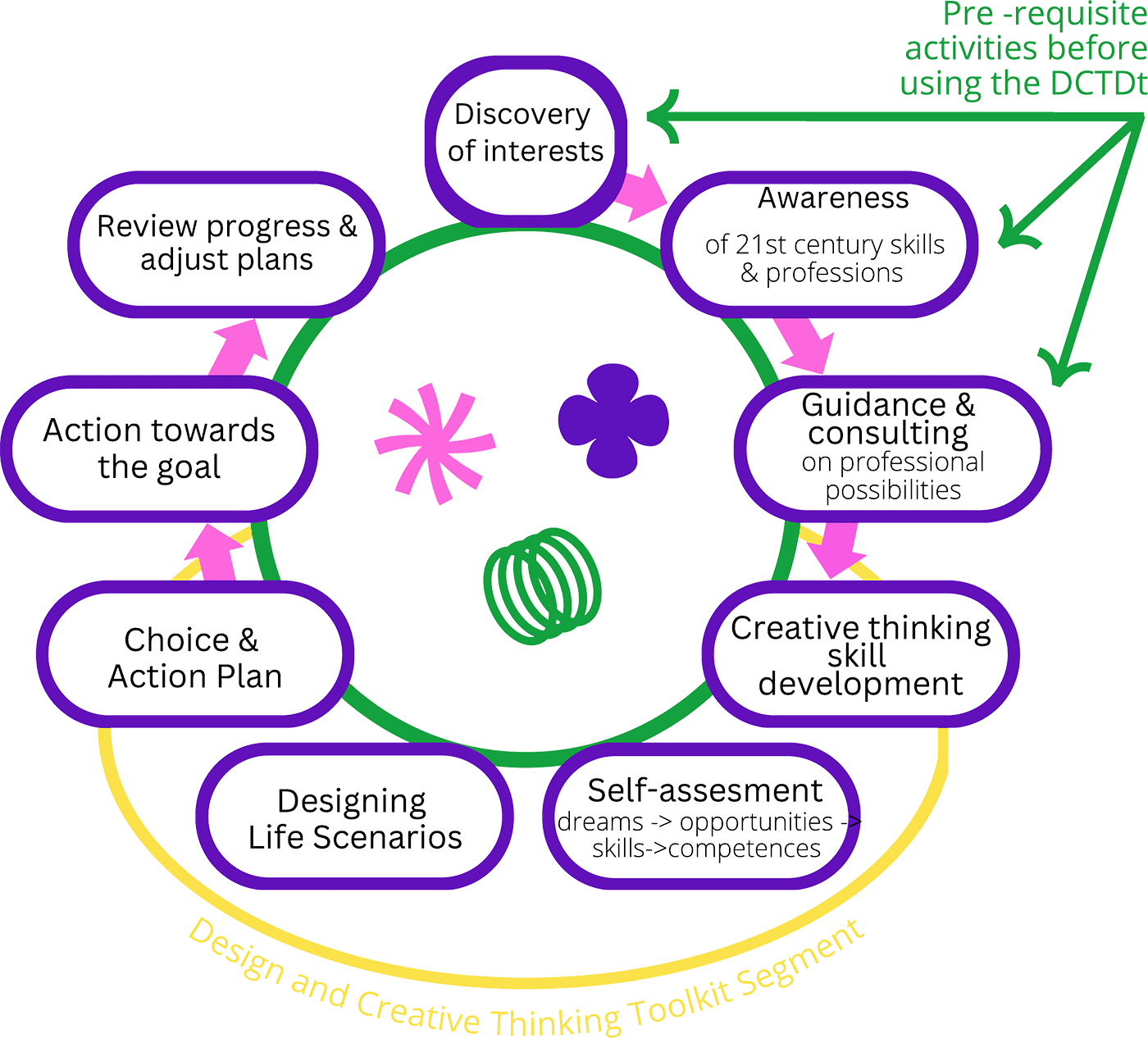
What is it?
Design and Creative Thinking Development Toolkit is a set of methods and activities. The toolkit consists of nine consecutive steps divided in two parts: the first part focuses on understanding and developing the concept of creative thinking skills, the second part focuses on the practical application of design and creative thinking skills in the decision- making process.
The toolkit was created with the intention of helping youth to understand how personality traits, interests and abilities can be successfully combined when choosing future professional directions in life. The activities are planned in such a way that the adolescent can design life scenarios in different professional directions, be able to make informed decisions about the growth path after obtaining basic education: continue studies, learn a profession or start working. Awareness of opportunities helps to navigate better complex situations, understand the sequence of events, see non-standard solutions and make alternative choices. Creative and design thinking skills are crucial in this toolkit.
What it consists of?
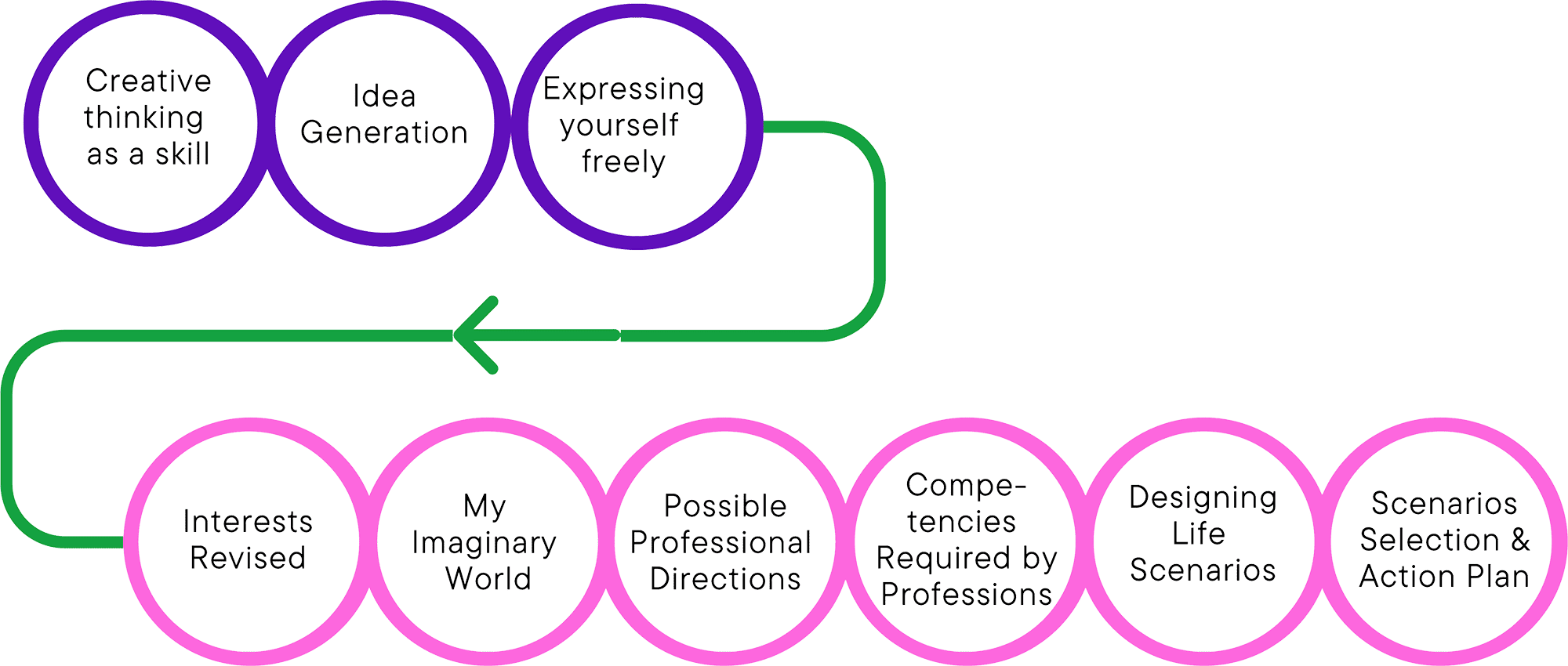
The process involves a set of consecutive stages: first, each participant is asked to evaluate the characteristics of own personality, talents and interests, and then is encouraged to create a vision of his/her future life and its quality. Initial step is followed by linking knowledge about professions with one’s own personality, helping the adolescent to identify possible professional directions to express oneself as well as providing the desired level of quality of life. Once three most interesting professional directions have been identified and some essential competencies required by these professions clarified (possessed and to be developed), the process of designing life scenarios begins by visually depicting the result to be achieved and most important things to be done towards it. The adolescent then chooses top priorities for the near future and prepares an action plan to get to know selected professions in depth and/or develop the necessary skills, so that after completing basic education, one can successfully continue to progress towards achieving the goals. The methodology provides an opportunity for regular evaluation of the implementation of the plan with the possibility of changing ones choice.
Creative Thinking Skills Development
The first three steps focus on the understanding and practical application of the concept of creative thinking. They will help form an idea of the versatility of creative thinking and develop the components that make up this skill: critical thinking, flexibility, freedom, originality, etc.
Designing Life Scenarios
The second part consist of successively performed stages, where personality traits, interests and skills are identified and evaluated, possible life scenarios with various professional opportunities are modeled, while helping the young person to discover the interactions of these factors.
Who is it for?
Primary target audience for the toolkit is youth aged 13 – 16 years, in the last grades of primary school (ISCED 2; most commonly grades 7, 8 and 9), in order to increase adolescents’ motivation, self-esteem, enhance growth mindset and help choosing further life scenarios.
Secondary target audience is a person of any age willing to explore alternative professional pathways, learn to make decisions by evaluating different perspectives, and dare to choose unconventional solutions.
Why to use it?
Current education systems around the world are dominated by a fixed way of thinking. Youth have lost motivation, confidence in themselves and their skills, leading to the emergence of categories such as NEETs (Young people not in employment, education or training), because their knowledge and skills often do not match the real demand of the labor market.
Youth, especially early and middle-aged adolescents have proven to have higher brain plasticity, hence it is crucial to develop skills and behavioural patterns a person will be able to use in adulthood.
The way of thinking (mindset) that correlates with creative thinking is the growth mindset. Carol Dweck, a professor at Stanford University, emphasises that it is extremely important for teenagers and young people to understand that making mistakes is a process, not a judgment and not an end result (Dweck, 2006). Design thinking tools that focus on visual and spatial thinking have a strong effect on changing perspectives and are relatively easy to implement among adolescents.
How to use it?
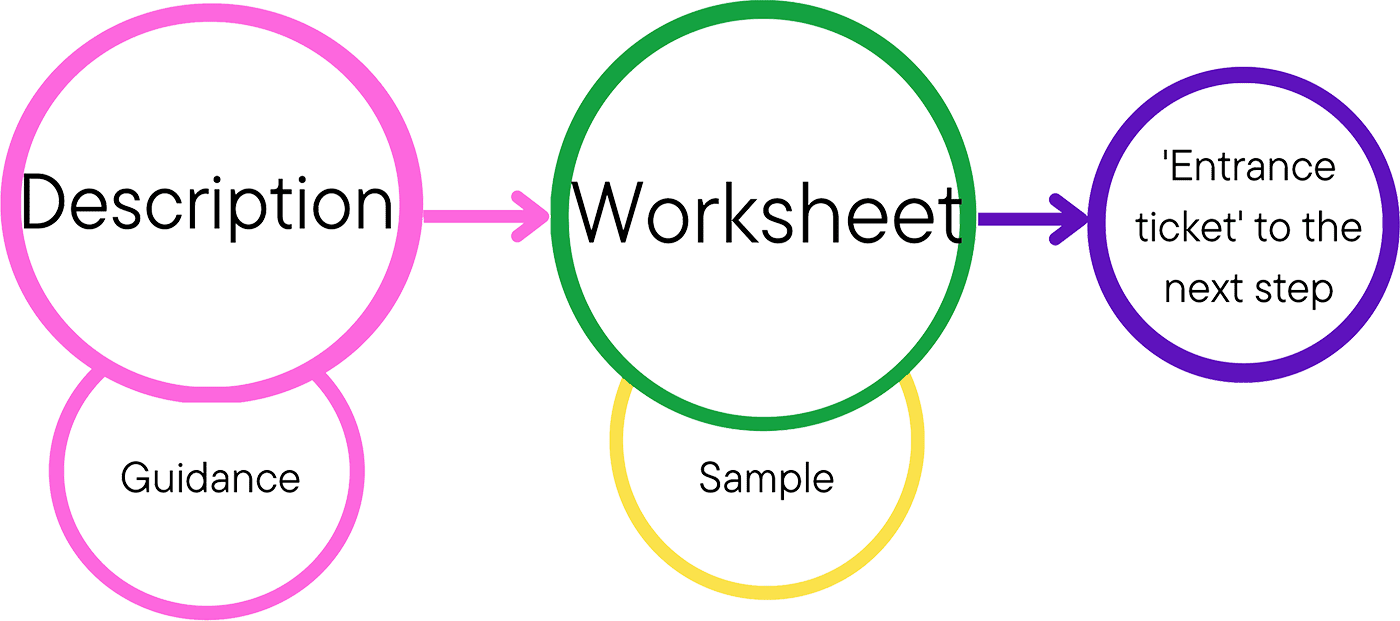
Read the description > get familiar with the tasks on the worksheet > fill in the worksheet > move to next step. Make sure all steps are completed sequentially. Do not skip one.
What are gains?
The toolkit is aimed to master the skill of obtaining and analysing available information both from the outside world and personal characteristics: personality traits, skills, interests, talents and to be able to consciously design different scenarios depending on the decision made about the chosen profession, education, through creative and design thinking.
Creative and design thinking skills evoke awareness of multiple choice opportunities and help to navigate better in complex situations, understand the sequence of events, see non- standard solutions and make alternative choices.
As a result youth will be able to create several life scenarios of their future life and embody the selected wellbeing aspects. In the development process, the adolescents will visually depict the achievable results and most important steps towards the goal. These activities will help to understand better the regularities between different aspects of the quality of life and the importance of personal contribution.
Remember – small gains add on later!
Design & Creative Thinking
Competence based on productive generation of new ideas as well as evaluation and improvement of existing ideas, which can result in original, effective solutions. (OECD, 2022)
“Creative thinking inspires ideas. Ideas inspire change”
Barbara Januszkiewicz
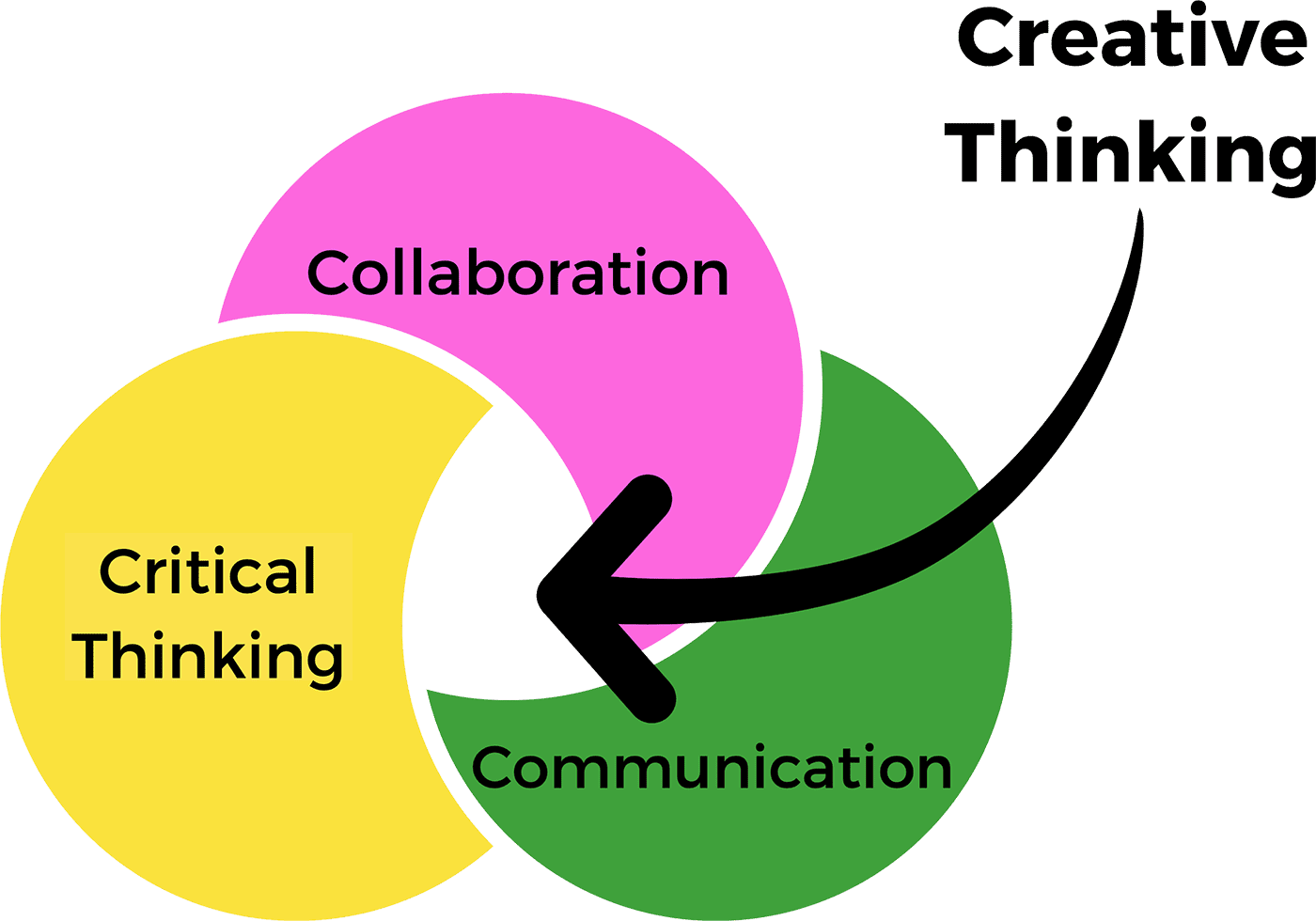
Creative thinking skill is not limited by demographic or social criteria. It can be developed by anyone to varying degrees. Moreover, creative thinking contributes to the development of other skills, including analytical and critical thinking, problem solving, cooperation and communication skills, promotes the strengthening of personality traits, improves academic performance and professional development .
Design thinking will be used as an umbrella method within this tool – starting with research, defining a problem or goal, generating ideas, prototyping them and analysing possible results, teaching and training young people to use the design thinking approach in various situations.